Fiat means “it becomes official because an authority declares it so.”
You’ll spot this word in two totally different places: a headline saying a rule was made “by fiat,” and a crypto post talking about “cash out to this currency.” Same word, different meaning, so it’s easy to get confused.
If you’ve been wondering what does fiat mean, you’re in the right place. In this guide, you’ll learn its meaning in plain English, its definition in law and money, and the simple clues that tell you which one a writer is using.
By the end, you’ll be able to read “fiat” once and instantly know whether it’s about power, currency, or something else.
Featured Snippet Answer
What does fiat mean? It means “it happens because an authority says so.” In everyday language, it can mean an official order. In money, fiat currency is government-issued money that people accept. Because it is legal tender and widely trusted, like dollars, euros, or rupees.
Quick bullets
- Fiat (general): An official order or command
- By meaning: “By order,” not by agreement
- Money meaning: Government-issued money used every day
- Currency meaning: The same as fiat money
- Cars): Fiat is also a car brand
Fiat Meaning: The 3 Main Uses
When people wnat to know “fiat meaning”, they usually mean one of these:
A) Fiat = an order (law and rules)
It can mean a command from someone with power. It often sounds formal.
- Example: “The policy changed by fiat.”
B) Fiat money / fiat currency = government money
In finance, this money meaning is clear: it is the normal money issued by a government.
- Example: “The US dollar is a fiat currency.”
C) Fiat = the brand name
It is also a car company name.
- Example: “He drives a Fiat.”
Tip: If the text is about banks, inflation, or crypto, “fiat” almost always means currency, not the car.
By Fiat Meaning (Simple Explanation + Examples)
Many readers search “by fiat meaning” or “meaning of by it”
It means a decision made by authority, not by vote or agreement.
This phrase is common when someone wants to highlight a top-down choice:
- “The rule was imposed by fiat.”
- “The change happened by fiat, not by discussion.”
- “The schedule was set by fiat.”
Close alternatives you can use:
- “by order”
- “by decree”
- “unilaterally”
- “without a vote”
What Is Fiat Money and What Is this Currency?

What is fiat money?
It is money that works because a government declares it valid and people accept it for payment.
What is fiat currency?
What is this currency? It means the same thing as fiat money. It includes:
- cash notes and coins
- the money in your bank account
- the balance you spend with cards and apps
Examples of this currency: USD, EUR, PKR, INR, GBP.
Authority Layer: Legal Tender + Central Bank Role
Legal tender meaning (slightly deeper)
Legal tender is the money a country recognizes for settling debts under its laws. In daily life, stores can have payment rules, but legal tender matters most for debts, contracts, and the legal system.
What does a central bank do?
A central bank helps keep the money system steady. It aims to protect:
- price stability (inflation not too high)
- financial stability (banks and payments keep working)
- trust in the currency
Monetary policy
Monetary policy is how a central bank guides the economy using money tools. The main tool is the interest rate, which affects borrowing and spending. Central banks may also buy or sell government bonds to add or remove money from the system. The goal is usually to balance growth with stable prices.
A Short History: Gold Standard, 1971, and Modern Fiat
To understand fiat vs gold, it helps to know the timeline.
What was the gold standard?
Under a gold standard, money was tied to gold. In some systems, currency could be exchanged for a fixed amount of gold.
What changed in 1971?
In 1971, the United States stopped converting dollars into gold for foreign governments. Often called the “end of Bretton Woods” or the “Nixon shock”. After that, major currencies moved toward this modern systems, where money is not fixed to gold.
Why did modern fiat spread?
This made it easier for governments and central banks to respond to recessions, wars, and banking crises. Today, most countries use fiat currency as the standard system.
What Does Fiat Mean in the Bible?
In the Bible, “fiat” means “let it be done.” It is a Latin verb used in the Vulgate (the Latin Bible) to show a word of power: God speaks, and something becomes real. It is also used for a deep act of faith, when a person accepts God’s will.
Where “fiat” appears (key verses)
| Bible moment | Vulgate phrase | Simple English meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Creation | “Fiat lux” (Genesis 1:3) | “Let there be light.” |
| Mary’s yes | “Fiat mihi…” (Luke 1:38) | “Let it be to me…” |
| The Lord’s Prayer | “Fiat voluntas tua” (Matthew 6:10) | “Your will be done.” |
What it teaches
- In Genesis, “fiat” points to God’s creative command, He speaks, and creation responds.
- In Luke 1:38, “fiat” is Mary’s yes to God’s plan, often called “Mary’s fiat.”
- In Matthew 6:10, “fiat” expresses surrender to God’s will in prayer.
Why Fiat Money Has Value
People often ask “why this money has value” or say, “Is fiat backed by nothing?”
This money is not backed by gold in most countries, but it still has strong support:
- Law and legal tender rules
- Taxes (people need the currency to pay taxes and fees)
- Trust in institutions (courts, banks, central bank)
- Network effect (money works best when everyone uses the same unit)
So, the better question is not “Is it real?” The great question is: Can the system manage well?
How Does Fiat Money Work? How It Is Created
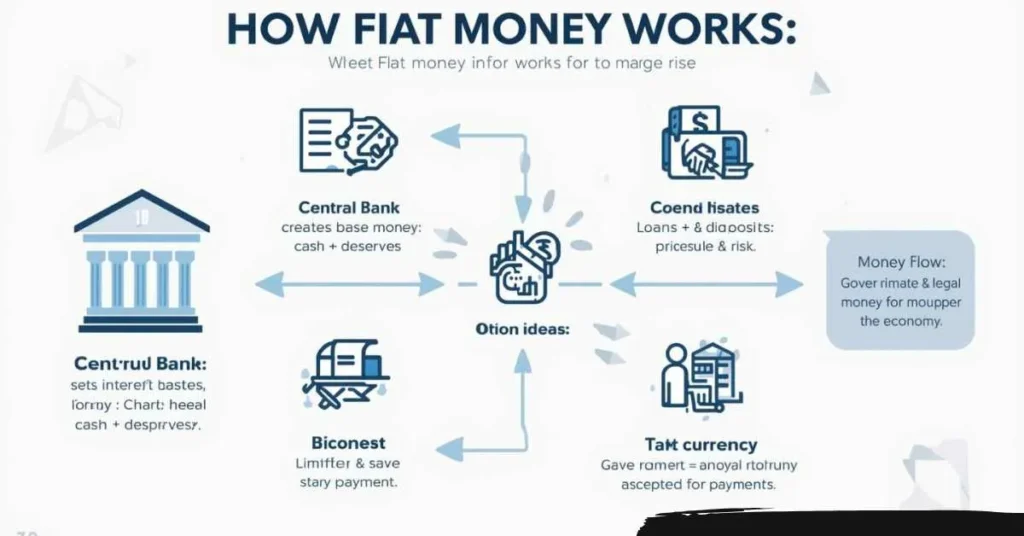
People also search “how does fiat money work” and “how fiat money is created.” Here is the clean version:
A) Central bank money (the base layer)
A central bank can create money like:
- cash
- bank reserves (money banks hold at the central bank)
It also sets key conditions, mainly through interest rates.
B) Bank lending (spendable deposits)
When banks lend, they often create new deposits in the borrower’s account. That increases spendable money in the economy.
Important: banks have limits (rules, capital, risk checks). And when loans are repaid, deposits can shrink.
C) Government spending and taxes (money flow)
Government spending puts money into the economy. Taxes pull money out. These flows affect demand, growth, and sometimes inflation.
Real-World Example: When Fiat Is Stable vs When It Breaks
Fiat systems can look very different across countries.
Stable example (normal life)
In many stable economies, inflation is kept low enough that prices do not change too fast. People can plan savings, salaries, and business costs with less fear.
Hyperinflation example (when trust collapses)
In some countries, trust breaks due to political crisis, war, or extreme money printing. Prices can rise daily, and people rush to spend money quickly. That is hyperinflation. It is rare, but it shows why trust and good policy matter.
Key point: Fiat is a tool. Results depend on how it is run.
Comparison Tables Fiat vs Crypto
Fiat vs Gold (Fiat Money vs Commodity Money)
| Feature | Fiat Currency | Gold / Commodity Money |
|---|---|---|
| Backing | Law + trust + economy | Physical commodity value |
| Supply | Can expand with policy | Limited by mining/reserves |
| Flexibility | High (crisis response) | Low (more rigid) |
| Inflation risk | Depends on policy | Can still inflate/deflate |
| Day-to-day use | Very easy | Harder to use directly |
Fiat vs Crypto (Fiat Currency vs Cryptocurrency)
| Feature | Fiat Currency | Cryptocurrency |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized (state/central bank) | Network + protocol rules |
| Price stability | Usually steadier | Often more volatile |
| Acceptance | Used for taxes and bills | Varies by place/platform |
| Consumer protection | Often stronger | Depends on custody/platform |
| Common use | Payments, salaries, pricing | Transfers, apps, investing |
Note: Stablecoins are crypto tokens designed to track fiat (like USD). They are not fiat, but they act like “fiat inside crypto” for many users.
How to Use “Fiat” in a Sentence
Authority meaning
- “The rule changed by fiat.”
- “The decision was made by fiat, not by vote.”
Money meaning
- “He converted crypto to fiat currency.”
- “Fiat money is used to pay taxes.”
Car meaning
- “She owns a Fiat.”
Cheat sheet
- By fiat = by order
- Fiat money / fiat currency = government-issued money
- Fiat = car brand (context: cars)
Expanded FAQ
Is fiat money the same as cash?
Cash is one form of fiat money. It also includes digital money in bank accounts.
Is fiat money backed by gold?
In most countries today, no. Modern systems do not promise fixed gold exchange.
Is fiat money backed by anything?
Not by gold, but it is supported by law, taxes, trust, and the economy behind it.
What does fiat mean in crypto?
In crypto, itmeans normal government money like dollars or rupees. “Cash out to fiat” means convert to bank money or cash.
Can fiat currency fail?
Yes, in rare cases. Trust can collapse during crisis, leading to very high inflation or hyperinflation.
Why do people prefer crypto over fiat?
Some prefer crypto for independence, fast transfers, or fixed supply. Others avoid it due to volatility.
Advantages of fiat currency?
It is easy to use, scales with the economy, and allows crisis response.
Disadvantages of fiat currency?
It can lose purchasing power in high inflation and depends on trust in institutions.
Conclusion:
So, what does fiat mean? In plain words, it means something is accepted because authority declares it and in law, it appears as by fiat meaning “by order.” In finance, fiat money or fiat currency is the government-issued money people use every day.
If you remember one line, use this: It works because people accept it, supported by law, taxes, and trust.
Read Also This Post: What Does Hotty Toddy Mean? Complete Explanation

Hello! I’m Clara Lexis, creator of Meanpedia.com. I specialize in breaking down words, phrases, and idioms so that anyone can understand and enjoy the beauty of English. My goal? Making language approachable, fun, and meaningful, one word at a time.